How to EQ Bass
Intro
For somebody who’s new to mixing music, it may be exhausting for them to listen to a track and know which frequencies to spice up or minimize to make the bass sound good in a song.
If you’re a beginner then one of the simplest ways is to guide you to know where to chop or increase important frequencies for a number of instruments. For this post, I’ll offer you some helpful eq frequencies for the bass sound.
However keep in mind, music production is all about tweaking and testing what’s going to work best for the track you’re presently working on. There is no one size suits all, every track would require completely different settings.
Helpful Bass Eq Frequencies
There’s a lot you possibly can sculpt with bass EQ – well, there may be much more frequency range than you would possibly assume. Without going overboard, listed below are eight ranges and easy spots on how to eq bass without any issues.
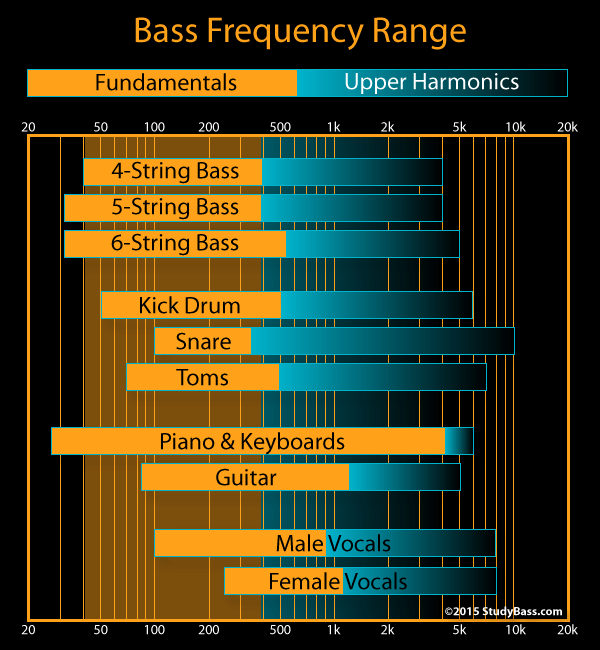
- Boomy (40 Hz – 90 Hz)
- Fat (75 Hz – 150 Hz)
- Thin (40 Hz – 180 Hz)
- Power (40 Hz – 150 Hz)
- Impression (40 Hz – 150 Hz)
- Readability (190 Hz – 800 Hz)
- Presence (800 Hz – 6.5 kHz)
- Attack (120 Hz – 4.1 kHz)
These first 5 are all sub-200 Hz. Nonetheless, take a look at what you are able to do above that. Presence and attack can attain as far as 6.5 kHz.

Bass Eq Suggestions
Before including an eq in your inserts it’s essential to have some vision/concept of the end outcomes. It is extremely necessary to perceive why you’re including an eq to bass or another sound.
Not an awful motive like “I would like it to sound better…” or “because so and so stated I need to increase 4kHz to make the bass notes more clearer”, which is true, however, it’s important to watch out because 4kHz is the place you additionally discover the kick drum presence and punch as well. So they may conflict.
Use the eq frequency list above to find out what must be performed to the bass of your track in order that it sounds good within the mix.
Don’t increase the excessive frequencies (treble) hoping the bass will sound brilliant, it’s a bass sound so something above 5kHz just isn’t at all times obligatory. Boosting the treble won’t make it bright as an alternative it is going to change into high-pitched and piercing.
It’s additionally not at all times obligatory to chop out the muddiness and by no means increase the mud either. Round 250Hz to 500Hz is the place you discover the growl of a bass, minimize that to get your bass sounding clear if it’s essential to.
Utilizing a digital mixer with the flexibility for a number of areas of boosts and cuts, you are able to do a lot. However, what are you able to do with the analog boards? Analog boards are available quite a lot of EQ designs, from a single sweeping mid-design to sweeping mid’s for “excessive mids” and “low mids.”
Within the case of the one sweeping mid, deal with readability and/or presence. In the case of mixers with the two sweeping mid’s, you’ve received fairly a bit more to work with. Ultimately, when you’ve got restricted EQ control, deal with clarity, presence, and the fat/thin.
If you aren’t certain where to begin, begin by listening to a set of songs that you like. Listen to the sound of the bass. Make notes on the way it sounds. Now, you’ve received a sound purpose.
A tip on bass EQ; don’t neglect the volume management. I’d had instances where I appreciated the mix however it appeared it didn’t match. Reducing just a few dB’s put it completely into the mix.
How to EQ Bass – Tips
Each Track is Distinctive – It should be said that each bass guitar recording, whether or not recorded with a microphone on the amplifier, direct-injected into an audio interface, and even a big stand up bass would require distinctive EQ settings. Even the very same bass guitar recorded 15 minutes later will find yourself needing barely different changes. Part of this is so much fun because you are learning how to eq bass for many different signals
Mix With Your Ears – I say to emphasize that, while a lot of the following pointers may be adopted broadly each time, the specifics might want to change. And no person can let you know precisely what to do at that level of detail. You’ll have to focus on your ears to make the fitting choices!
Work in Solo & in Context – When doing precision work to form the bass tonal traits themselves, you may want to pay attention in solo mode for probably the most part so that you simply only hear the bass guitar. When making broad choices listen to the bass together with the total mix. When balancing the bass versus another instrument, you possibly can solo them both so that you only hear them in distinction with each other.
Use Headphones or a Subwoofer – If in case you have acoustic treatment (particularly bass traps) in your mixing room and the finest studio subwoofer you will get your hands on, use these. In any other case, you may want a set of studio headphones with a frequency response that reaches as low as possible. If you cannot hear the low-end clearly, then you possibly can’t make the fitting choices.
Conclusion
As you possibly can see, the bass guitar has a variety of frequencies that are used and you’ve got loads you are able to do with them. Not only will EQ bring out the fitting sound but compression and gating also can assist considerably with the sound.
The bass is simply as necessary as a rhythm guitar and, with a little work, you may make your mixes sound even better! Check our article on how to use Pitch Correction plugins here!
Check our eBook on Mixing Tips! If you want to get a more in-depth breakdown of those tips we share, follow our link and get the “Ultimate Mixing Tips Booklet” and up your game quickly!
Best Mastering Equalizers: Shape Your Final Frequencies!
Best 500 Series Equalizers: Top 10 Models To Shape Your Frequencies!
Bettermaker Stereo Passive Equalizer Review: New Pultec-Style Equalizer!
Heritage Audio Motorcity EQualizer Review: Amazing 7-band Mono Passive EQ!
API Select SV14 Review: Great New 500 Series EQ from API! (2023)






