What is a MIDI
Intro
MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) is a protocol developed in the 1980s which permits digital instruments and different digital musical tools to communicate with one another. MIDI itself doesn’t make sound, it’s only a sequence of messages like “note on,” “note off,” “note/pitch,” “pitchbend,” and lots of extras.
These messages are interpreted by a MIDI instrument to supply sound. A MIDI instrument generally is a piece of hardware (digital keyboard, synthesizer) or a part of a software program environment (Ableton, Garageband, digital performer, logic…)
Some great benefits of MIDI include:
compact -entire music will be saved inside a couple of hundred MIDI messages (in comparison with audio data which is sampled thousands of times a second)
easy to modify/manipulate notes -change pitch, duration, and different parameters without having to rerecord
change instruments -remember, MIDI solely describes which notes to play, you may send these notes to any instrument to vary the general sound of the composition.

What is a MIDI and how does it work?
No audio signals (sounds) are despatched via MIDI. As an alternative MIDI works as a digital signal. A sequence of binary digits (0s and 1s).
Every instrument (or laptop) understands and then responds to those 1s and 0s, that are mixed into 8-bit messages supporting knowledge charges of as much as 31,250 bits per second.
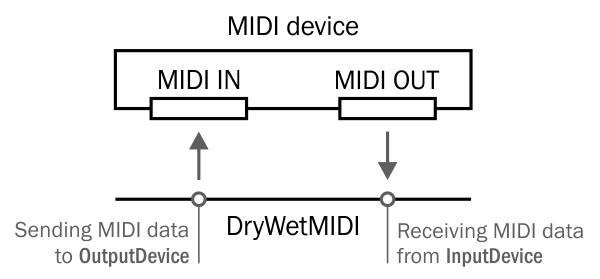
These messages can communicate useful info similar to:
- which note is pressed
- the second a note is pressed and launched
- the rate (how hard it’s pressed)
- after-touch (when key pressure changes)
- vibrato, and even;
- pitch bend,
The MIDI ‘protocol’, as it’s recognized, can support as much as 128 notes, starting from C 5 octaves beneath center C up to G ten octaves higher. So just about any note, you would ever want to play.
Different values similar to velocity are recorded as numbers between 0 and 127. With a 0 being no sound and 127 being the loudest.
These standardized numbers will be read by any instrument or machine able to understanding MIDI. Which is why MIDI is such a robust device in music production.
Maybe the easiest way to understand what MIDI is to first understand what it’s not:
MIDI is nothing more than data – a set of directions. MIDI data accommodates a listing of events or messages that inform an electronic gadget (musical instrument, laptop sound card, cellphone, et cetera) easy methods to generate a certain sound.
At this time, there are particular MIDI controllers – nonetheless principally keyboards — that come geared up with a number of knobs and faders to manipulate the devices they’re emulating or controlling. These MIDI controllers do not include tons of preloaded sounds and effects because they generate all of their audio by way of third-party hardware and software programs.
MIDI controllers, like MIDI synthesizers, are available all styles and sizes. There are MIDI controllers that appear to be guitars, clarinets and drums. Plus there are particular foot pedals and elaborate control consoles with dozens of knobs and faders for skilled high-quality mixing. There are even particular MIDI consoles to regulate stage lighting during a show.

MIDI Cables
MIDI data is totally different from the audio. Due to this fact, we can use conventional audio cables to transmit MIDI data. As an alternative, we use particular MIDI cables, which have 5 miniature pins. This is one of the differences in what is a MIDI and it’s whole concept
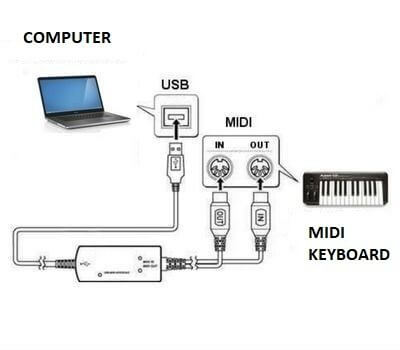
MIDI can be communicated over USB. This may occur in a couple of other ways. One way is that you can send MIDI data to a MIDI interface that’s designed for this actual process.
MIDI interfaces can be considered translators. They convert MIDI data to directions that a computer can learn. The interface then sends the information to your DAW by way of USB.
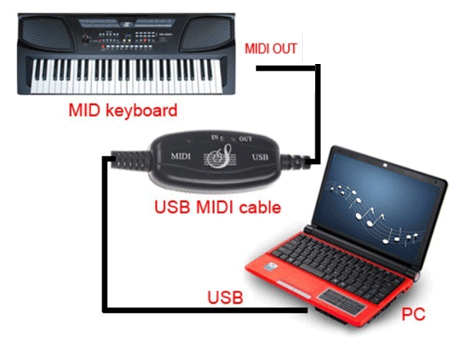
Alternatively, you need to use a selected MIDI-to-USB cable. It enables you to bypass a MIDI interface and send the information instantly out of your device to the pc.
The cord has a MIDI plug on one end and a USB plug on the other. Some MIDI gadgets even have their very own USB ports that mean you can use a USB-to-USB cable.
To find out the most effective method for your devices, consult the guide or specs in your MIDI controller.
The best way to use MIDI in your music
MIDI can play a number of totally different roles in your productions. You’re most likely aware of a few of them already.
To get began it would even be extra useful to clear up what MIDI isn’t.
MIDI never transmits an actual audio signal—it’s info only. That implies that if a MIDI keyboard doesn’t have an onboard sound supply like a synth or sampler, it won’t make any sound!
While you connect a MIDI controller to your DAW to play digital instruments, you’re merely feeding them actual time MIDI info.
The same is true whenever you sequence MIDI in your DAW and send the data to hardware gear like an analog synth or drum machine.
The largest advantage of MIDI is you could simply edit performances note by note, change their articulation, and even alter or substitute the sound that plays them!
However, that’s not all. You can control much more than simply notes using MIDI. Many options of a standard musical performance have an equal in MIDI.
You can even use it to automate parameters or change patches on hardware or software program devices or effects. That’s what is a MIDI is all about!
Master your MIDI setup
Now that you know what is a MIDI, it’s time to integrate it into your personal studio workflow.
MIDI offers you entry to each sound you may consider and all of the enhancing energy it’s good to make your music production quick and seamless.
Go experiment and discover your favorite methods to work with MIDI.
Check our eBook on Mixing Tips! If you want to get a more in-depth breakdown of those tips we share, follow our link and get the “Ultimate Mixing Tips Booklet” and up your game quickly!






